Game changing new Toshiba EV Battery can add 320kms of range in just 6 minutes of charging

One of the final hurdles in the uptake of electric cars may be overcome with the latest news coming out from electronics giant Toshiba. The dreaded “range anxiety” is becoming a thing of the past as most car manufacturers have generally overcome that but battery charging times, particularly if you are on a long road trip, is still seen as an issue. Fast charging stations such as the Tesla Supercharger can add 300km range in about 20 minutes but compared to a conventional car where you can do that in just a few minutes in reality that is still “slow”.
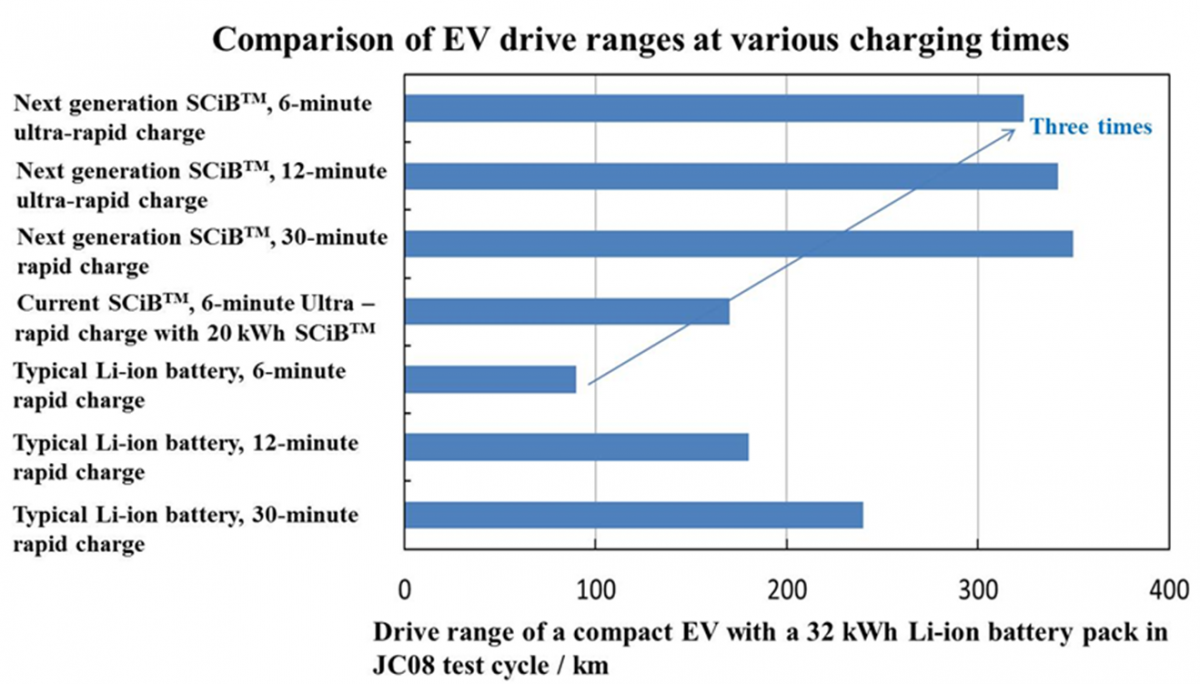
Toshiba has developed a new SCiB battery that they claim can enable electric cars to add 320 km of range with just 6 minutes of charging. The new anode material used in the battery is a titanium niobium oxide that is able to provide twice the capacity of the anode used in current lithium-ion batteries.
The new battery gives both high energy density and ultra-rapid charging and its titanium niobium oxide anode is much less likely to experience lithium metal deposition during ultra-rapid recharging or recharging in cold conditions which is a cause of battery degradation and internal short circuiting.
 Prototype of 50Ah next-generation SCiBTM 111mm x 194mm x 14.5mm
Prototype of 50Ah next-generation SCiBTM 111mm x 194mm x 14.5mm
Toshiba’s current SCiB employs a lithium titanium oxide anode, and is known for excellent operating characteristics in respect of safety, long life and rapid charging. It has found wide use in vehicles and industrial and infrastructure applications, including automobiles, buses, railroad cars, elevators and power plants. The high energy density of the battery, and its rapid recharging, have made important contributions to enhancing the convenience and promoting the spread of EV.
Building on this heritage, Toshiba has developed a proprietary method for synthesizing and disarranging crystals of titanium niobium oxide and storing lithium ions more efficiently in the crystal structure. The anode of the next-generation SCiB realized through this approach has double the capacity of the anode of current lithium-ion batteries.
“We are very excited by the potential of the new titanium niobium oxide anode and the next-generation SCiB,” said Dr. Osamu Hori, Director of Corporate Research & Development Center at Toshiba Corporation. “Rather than an incremental improvement, this is a game changing advance that will make a significant difference to the range and performance of EV. We will continue to improve the battery’s performance and aim to put the next-generation SCiB into practical application in fiscal year 2019.”
Rigorous testing of a 50Ah prototype of the new battery has confirmed that it retains the long life cycle, low-temperature operation, excellent safety and rapid recharging characteristics of the current SCiB. The energy density by volume of battery is twice that of the current SCiB. The next-generation SCiB maintains over 90% of its initial capacity after being put through 5,000 charge/discharge cycles, and ultra-rapid recharging can be done in cold conditions, with temperatures as low as minus 10°C, in only ten minutes.
Toshiba say they will continue to develop higher energy density batteries that extend the range of EVs and support ultra-rapid recharging, and aims to commercialize the next-generation SCiB in 2019.
Source: Toshiba
